The essential guide to bonding composite materials
Composite materials can be the solution to many design problems, but bonding them can prove difficult without expert advice. In this article we explore the essential information you must have to bond composites to different substrates.
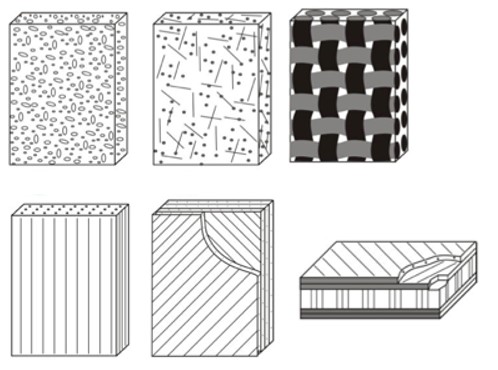
What is a composite material?
A composite material is a heterogeneous material, i.e., consisting of two or more phases with different physical properties, whose properties are much better than those of its constituent phases. Usually, the different phases in the composite are made up of different materials, such as in the case of composites of carbon fiber and epoxy resin
Gluing composite materials
Traditional coupling techniques such as welding or mechanical fastening often damage and weaken composite materials. As a result, adhesives have been the ‘thing that has revolutionized the use of composite materials in industries such as aerospace, automotive, wind power, and rail.
The ‘use of adhesives offers advantages such as even load distribution, shock absorption, high weight-to-strength ratio, reduction of galvanic corrosion, improved aesthetics, and bonding of different substrates. Provided the necessary precautions are taken, the use of adhesives to bond composite materials can provide a strong, lightweight, and aesthetically finished product. To learn more about the advantages of adhesives, compared with traditional fixing methods, read our product guide “What are structural adhesives?“

Adhesives for bonding composites
To choose the right adhesive for your needs, it is helpful to know 3 things about the material you choose. These are the modulus, required cohesive strength and shear strength. The compatibility of the composite material and the chosen adhesive can then be determined by checking these values against those of the adhesive.
It is essential that the stresses present in composite joints do not exceed the capabilities of the adhesive.
In general, however, different types of adhesives are suitable for different applications on composite materials. These types are explored below.
Epoxy adhesives such as Araldite are the most commonly used adhesives for bonding composites due to their excellent strength and durability, offering mechanical performance that can withstand high loads. Epoxy adhesives have “crash resistant” characteristics.
They are characterized by negligible shrinkage during curing, not stressing thinner substrates.
They are fast, developing mechanical performance also very quickly and have excellent environmental and weathering resistances.
Two-component polyurethane adhesives can be used for bonding large composite panels.



