ANTI FRICTION COATING MOLYKOTE®
Often described as “lubricating lacquers” or “dry lubricants,” MOLYKOTE® AFCs contain solid lubricants, rather than color pigments, dispersed in carefully selected resin and solvent mixtures. The choice of raw materials and the concentration of each ingredient are important for the customization of each Anti-Friction Coating in various applications.
MOLYKOTE® AFCs form a dry film and optimize the friction of metal, plastic and elastomer parts, even under intense loads and severe operating and environmental conditions.

OPERATING PRINCIPLES AND CONDITIONS
MOLYKOTE® Anti-Friction Coatings are particularly effective in boundary and mixed friction states, as illustrated by the Stribeck curve (Figure 1). In these states, direct metal-to-metal contact and wear occur because hydrodynamic fluid lubrication cannot be achieved.
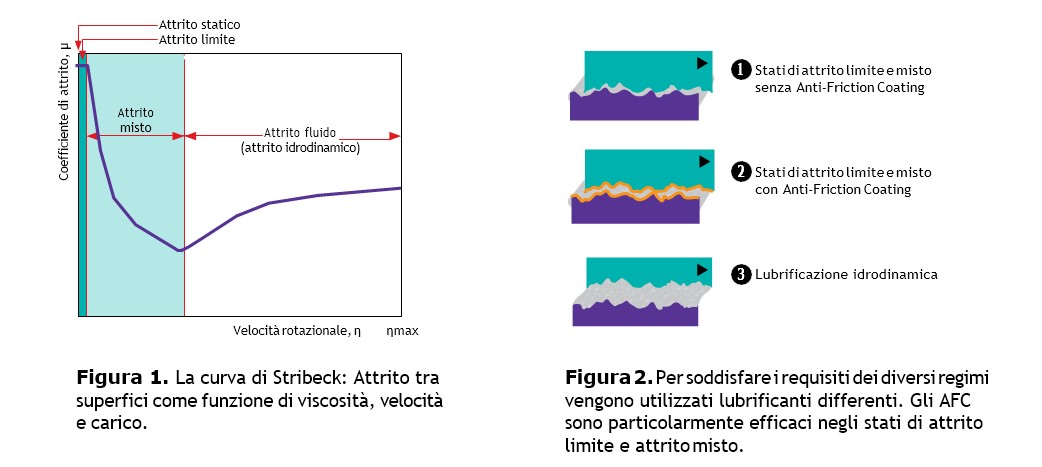
In MOLYKOTE® AFCs, solid lubricants are maintained on the substrate surface by the adhesion force of the resin, so that the surfaces are always separated by a dry lubricating film, effective both in oscillatory movements and at very low speeds or high loads. MOLYKOTE® Anti-Friction Coatings can also support hydrodynamic fluid lubrication as an agent to improve run-in. In addition, AFCs provide lubricating properties if the hydrodynamic lubricating film breaks down.
TYPICAL RUN-IN EFFECT AND FRICTION VALUES
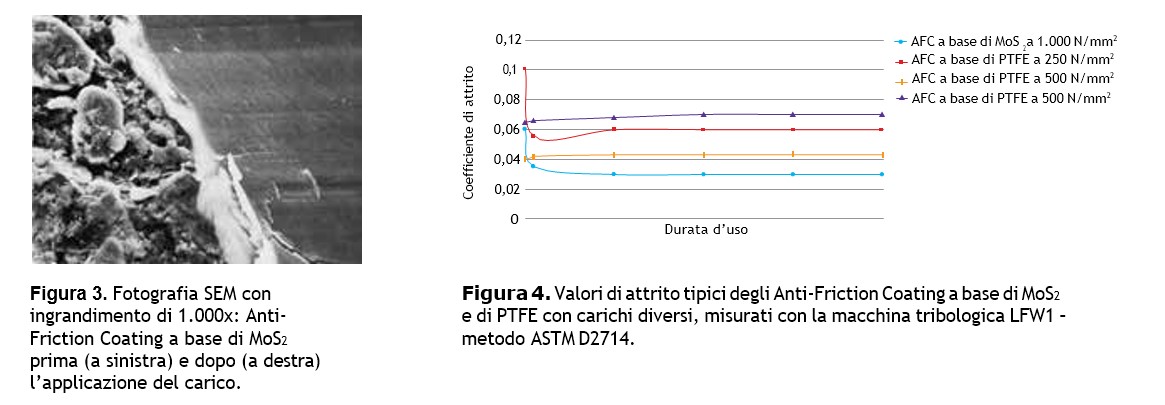
Anti-Friction Coatings generally are applied with a dry film thickness of 10-20 µm. Under load, the film structure is compacted, producing an extremely smooth surface that covers the roughness of the carrier material (Figure 3). The friction coefficients of MoS2-based Anti-Friction Coatings are compared with PTFE-based ones in Figure 4. The coefficient of friction of MoS2-based Anti-Friction Coatings is reduced after a short break-in phase.