ADHESIVES for electric motors
Why electric motors should be assembled with Araldite structural adhesives
Electric motors are ubiquitous in everyday life. Due to technological advances, they have become smaller and more efficient, creating new technological challenges. Bonding offers many advantages in terms of production and operation, allowing engineers in design to choose from a wide range of adhesives to increase electric motor performance.
However, electric motors are not only used for emission-free driving, but are also found in window regulators and seat adjusters. In fact, they can be found everywhere-in electric bikes, in tools, even in our kitchens.
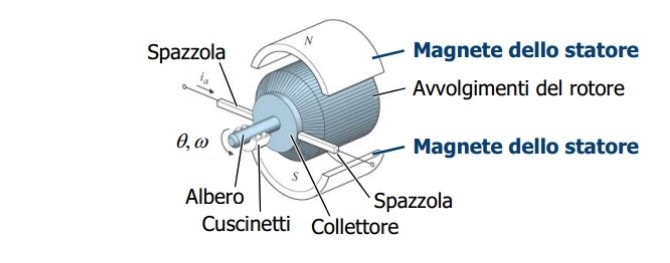
All electric motor manufacturers have a common goal in mind: to make them smaller and more powerful while increasing their efficiency. In striving to achieve this goal, engineers must consider many things: for example, the design of the lamination or an optimal insertion of the magnets into the lamination stack while leaving the smallest possible gap between the magnet and the coil.
Established methods of mechanical assembly are reaching their limits in terms of both the performance of the engine itself and the manufacturing process.
Araldite adhesives not only allow higher tolerances and prevent corrosion but also provide impact resistance, which is essential to withstand the high dynamic forces to which electric motors are subjected. Their vibration damping characteristics reduce noise and provide acoustic improvement. Due to an even stress distribution, the adhesives are able to compensate for thermal stresses that may be generated due to different coefficients of thermal expansion between the stator and housing; and in addition, their gap-filling properties help prevent slippage in the shaft area.
Araldite structural adhesives are particularly suitable for three steps in the assembly of electric motors:
- Assembly of magnets and lamination stacks,
- shaft and rotor assembly
- Assembly of stator and housing.
BENEFITS
- Replace mechanical fasteners to decrease parts and reduce costs
- Fill in the gaps (e.g., between stator and magnet and rotor to magnet) for lower tolerances
- Improve resistance to shock and vibration
- Improve adhesion to all magnetic materials
- Simplifies automated assembly
- Reduces vibration and noise
- Improves resistance to high temperatures
- Increase torque transfer
- Provide an even distribution of stress and load
- Preventing corrosion and environmental exposures
- Fill in the gaps, allow wider tolerances
- Reduce overall size and weight while maintaining equal performance




